If you’re dealing with the pain and discomfort of a bulging disc or a herniated disc, you’re not alone.
These common spinal conditions can affect both men and women of all ages — most prevalent among those ages 25-55.
But understanding the differences between a bulging disc vs. herniated disc is crucial when it comes to finding the right treatment.
We’ll explain the key differences between these two conditions, including causes, symptoms and treatment options for pain relief.
What Is a Bulging Disc?
A bulging disc, also known as a protruding disc, is a spinal disc that has extended beyond its normal boundary.
The spinal discs are soft, cushion-like structures located between the vertebrae in the spine. They help absorb shock and allow for flexibility in the spine.
A bulging disc can occur in any part of the spine but is most common in the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine) regions.
When a disc bulges, it may put pressure on your surrounding nerves and cause you pain or discomfort.
It may also lead to another conditions, such as sciatica or spinal stenosis.
What Is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a spinal disc that has ruptured or torn, allowing the inner fluid to leak out and press on surrounding nerves.
When a disc herniates, it may cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area.
A herniated disc is most common in the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine) regions.
It may also lead to another conditions, such as sciatica, cervical radiculopathy or loss of bowel control.
Bulging Disc vs. Herniated Disc: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between a bulging disc and a herniated disc is the degree of damage to the spinal disc — a bulging disc is a less severe form of disc damage than a herniated disc.
A herniated disc is generally considered to be more severe than a bulging disc because it involves a tear or rupture in the outer layer of the disc, which can cause the inner material to leak out and press on surrounding nerves.
Although it is considered more severe, most patients who experience symptoms related to an acute herniated disc will typically recover within 8-12 weeks without the need for invasive treatments.
Other differences between the two conditions include:
- Location: Both bulging and herniated discs can occur in any part of the spine. However, herniated discs are more likely to occur in the lower back (lumbar spine) or neck (cervical spine), while bulging discs are more commonly found in the neck and upper back (thoracic spine).
- Symptoms: While both conditions can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area, a herniated disc may cause more severe symptoms due to the pressure on the surrounding nerves.
- Treatment: Initial treatment for a bulging disc may involve rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques such as ice or heat therapy, medication, and/or steroid injections. For a herniated disc, the initial treatment is similar to the treatment for a bulging disc, but surgery may be considered if conservative treatments do not provide relief.
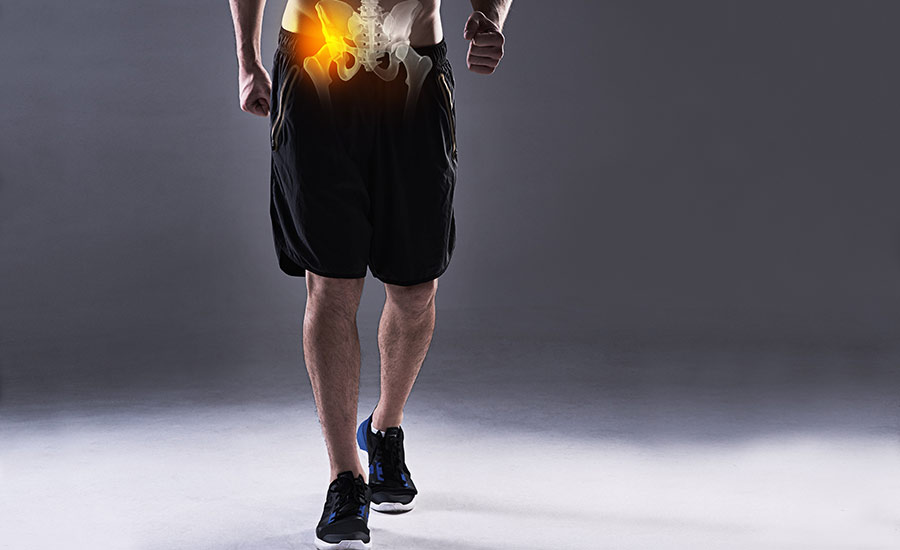
A herniated disc occurs mostly in the lower back, while a bulging disc occurs mostly in the neck and upper back
Bulging Disc vs. Herniated Disc Causes
The risk factors for developing a bulging disc and a herniated disc are similar, as both conditions involve damage to the spinal discs that cushion the vertebrae in the spine.
Risk factors for developing a bulging disc or a herniated disc include:
- Age: As you age, the spinal discs can degenerate and become more prone to bulging or herniation.
- Genetics: Some people may be more predisposed to developing herniated or bulging discs due to genetic factors.
- Excessive weight: Carrying excess weight can put additional stress on the spine and increase the risk of disc problems.
- Occupation: Bulging disc may be connected to physically demanding jobs that require repetitive lifting, bending, or twisting.
- Poor posture: Prolonged sitting or standing in an incorrect posture can put extra pressure on the spinal discs and increase the risk of bulging or herniation.
- Repetitive strain: Repeated movements or heavy lifting can put stress on the spine and increase the risk of disc problems.
- Trauma or injury: A sudden impact or trauma to the spine, such as a car accident or a fall, can cause a herniated or bulging disc.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to increased rates of disc degeneration and disc problems.
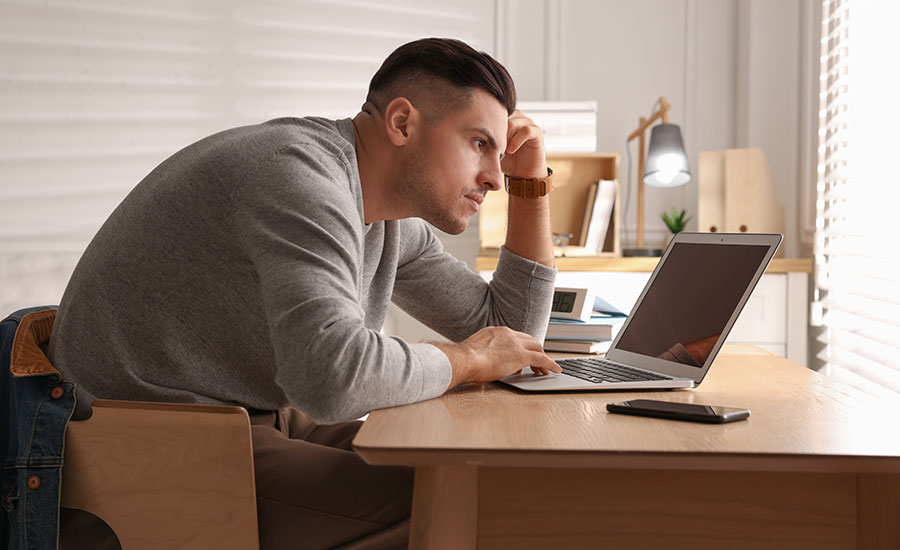

Bad posture while sitting in front of a computer is one of the causes of a bulging disc
Herniated Disc vs. Bulging Disc Symptoms
Herniated and bulging discs have similar causes and similar symptoms, so how can you tell which one you’re suffering from?
While both conditions can cause pain and discomfort, a herniated disc typically causes more severe and widespread symptoms, such as a sharp or shooting pain, due to the more significant displacement of the inner core of the disc.
Common symptoms of both a bulging disc and a herniated disc include:
- Pain in the affected area of the spine
- Stiffness or a decrease in range of motion
- Numbness or tingling in the affected area
- Weakness in the affected area
- Muscle spasms
- Reduced mobility or flexibility
- Having trouble standing or sitting for longer periods of time
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction, in severe cases
It’s important to note that not everyone with a herniated or bulging disc will experience symptoms. Additionally, the type of symptoms can vary depending on the location and extent of the disc problem.
Bulging Disc vs. Herniated Disc Treatment
A bulging disc and a herniated disc have similar causes and symptoms, which is why treatment options are typically the same or similar because they affect the same parts of the spine.
At OrthoEast, our physicians will find the best course of treatment for your pain based on your condition, medical history and similar factors.
Common treatments for both a herniated disc and a bulging disc include:
Pain Relief Medications
Pain medication can be helpful in managing the discomfort associated with both conditions.
Acetaminophen and ibuprofen, which are available without a prescription, can aid in lessening pain and inflammation. Our OrthoEast physicians may also recommend stronger prescription pain medication if the pain is more severe.
However, it’s important to note that pain medication alone cannot fix a bulging or herniated disc.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often recommended as a treatment option for herniated and bulging discs, as it can help relieve pain, improve mobility and flexibility, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
The type of physical therapy that’s right for you will depend on the severity of your condition and your individual needs. A physical therapist may design a personalized exercise program to address the specific areas of weakness and improve your overall muscle strength and flexibility.
For example, if you’re suffering from a bulging disc, sciatica stretches can help reduce stiffness and increase mobility in the affected area, while low-impact aerobic exercises such as swimming or cycling can help improve your overall fitness without putting additional strain on your spine.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care is a form of alternative medicine that involves the manipulation of the spine and other joints to improve overall health and alleviate pain. It is often recommended as a treatment option for herniated and bulging discs, as it can help reduce pressure on the affected area and promote healing.
During a chiropractic treatment session for a herniated or bulging disc, a chiropractor will typically use hands-on spinal manipulation techniques to carefully adjust your spine and reduce pressure on the affected area. This can help alleviate your pain and improve mobility in the affected area.
Apart from spinal manipulation, a chiropractor may utilize additional methods like massage, stretching, and exercise to alleviate pain and enhance overall functionality.
Epidural Steroid Injections
Epidural steroid injections are a treatment option for herniated and bulging discs in which a corticosteroid medication is injected directly into the affected area of your spine. This medication can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the affected area.
During an epidural steroid injection, we will use imaging technology such as an X-ray or fluoroscopy to guide the injection needle to the precise location of the herniated or bulging disc.
Once the needle is properly positioned, the medication will be injected into the epidural space around your affected nerve root.
Surgery
If more conservative treatments are not effective and your condition is severe and causing significant pain or disability, we may recommend surgery.
While a herniated disc is more likely to require surgical intervention, there are several surgical options for both herniated and bulging discs, including a discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion.
During a discectomy, the portion of the disc that is pressing on the nerve root is removed, while during a laminectomy, a small portion of the bone in the back of the vertebra is removed, to relieve pressure on the nerve root.
Spinal fusion fuses two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and reduce pressure on the affected area. (At OrthoEast, we also offer alternatives to fusion whenever possible).
Schedule an Appointment for a Bulging Disc or Herniated Disc at OrthoEast
If you are experiencing bulging disc or herniated disc pain that is not responding to conservative treatments, make an appointment with our spine specialists at OrthoEast. Our fellowship-trained, board-certified physicians specialize in orthopedic care and offer personalized treatment plans for every patient.
We’ll work together to find the root cause of your pain and determine the best option to ensure that you find long-term pain relief.
We offer convenient locations throughout New Jersey and New York, where we provide the highest quality of care.
Meet our physicians and find the pain relief you deserve to regain your quality of life.



